Downlink
Basic
Downlink is the way to send commands to your device device, for LoRaWAN we have 3 specifications known as classes.
You can learn more about LoRaWAN classes here: class A, class B, class C
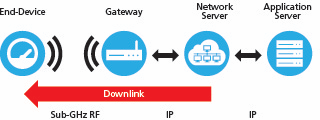
image from Semtech An example how downlink flow works, where "Application Server" is Kora
Downlink on Kora
A downlink is always attached to a device, under devices page when you open a device, you will find "Downlink" tab just above the map. downlink is a queue, so you can add multiple downlinks to be send.
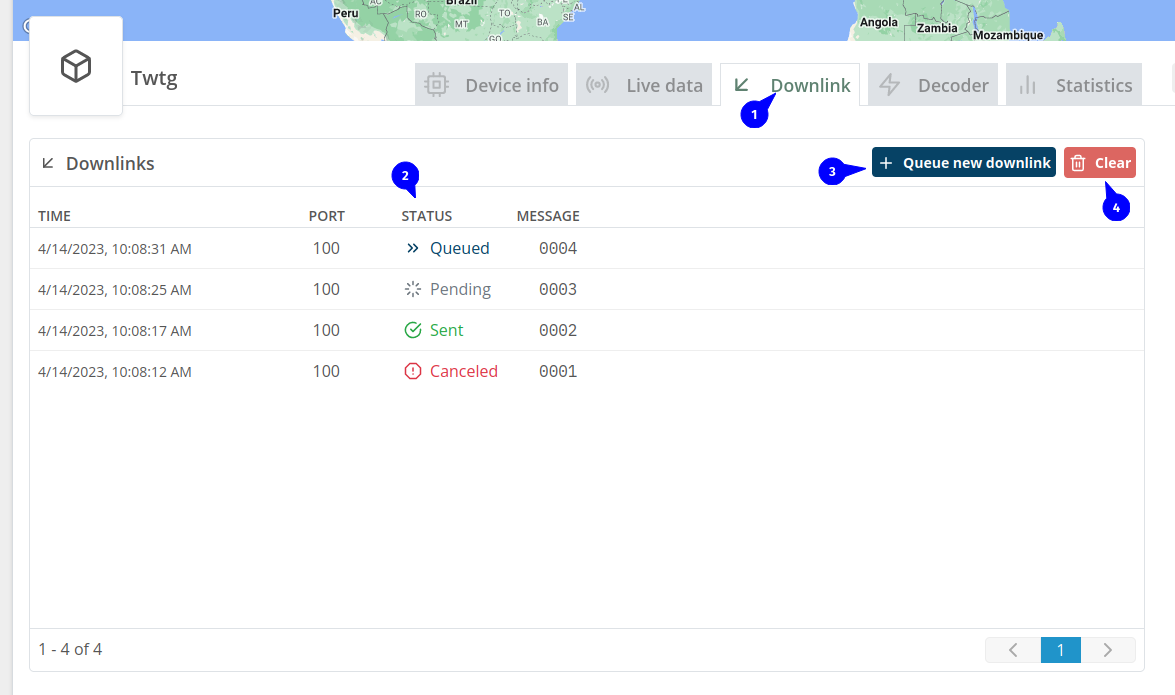
- Access to downlink page
- Downlink status
- Queue: Means that the downlink is on queue to be send.
- Sent: When the downlink was successfully sent to the device.
- Pending: This status happen when you create a confirmed downlink , it will change to "Sent" when the device confirm this downlink.
- Canceled: Cancelled happen when you click on "Clear" button(4) or when you create a downlink via public api, public api cancels every downlink with queue status.
- To create a new downlink
- Clear will remove all downlink from queue and set their status to canceled.
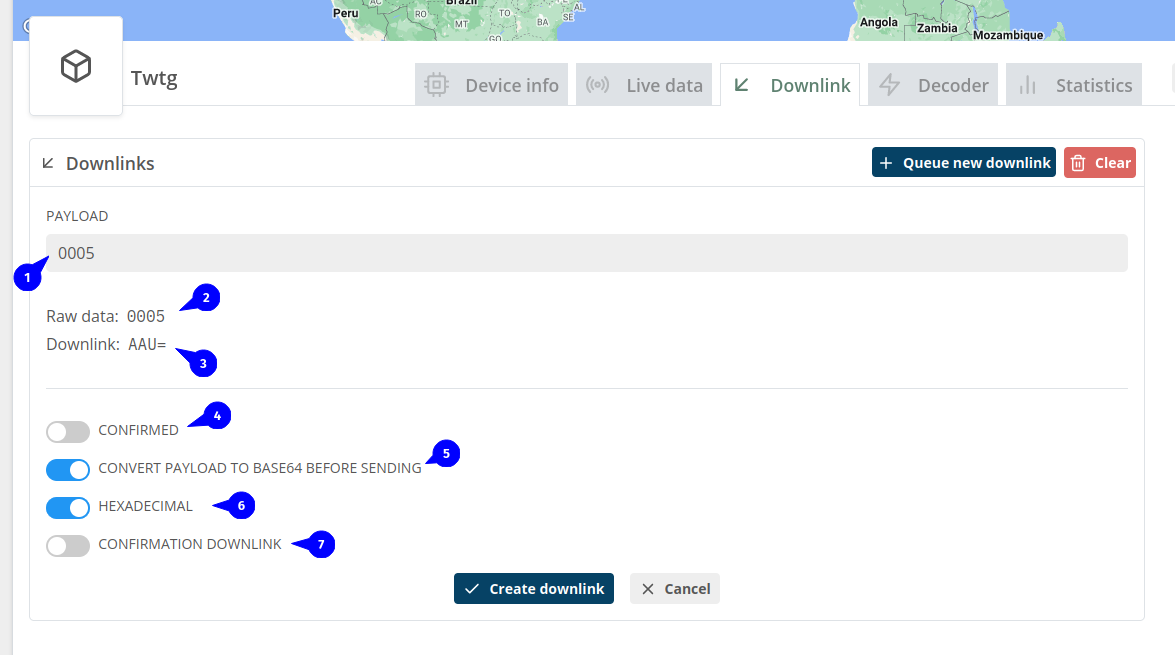
- Payload is the message to send to device, for Private LoRaWAN payload must be a hex string, you can put a base64 string and kora will convert it to a hex.
- Your payload in raw mode, it's makes more sense when you are using a template.
- Your payload after encoded.
- Confirmed downlink is related to a LoRaWAN specification, to understand confirmed downlink: class A, class B, class C, each class may have different behavior for confirmed.
- This will encode your payload to base64 format.
you can skip that if your device is Private LoRaWAN because of first point
- Tells that your payload is hexadecimal, this is important if you are using base64(5) encode, a regular string and hex is encoded different in base64.
you can skip that if your device is Private LoRaWAN because of first point